Home >
NDACC Spectral UV Instrument Working Group
>
Uncertainty Evaluation in Measurement and Modelling of UV Irradiance
Uncertainty Evaluation in Measurement and Modelling of UV Irradiance
A novel method to
estimate uncertainties in both measurements and results of radiative transfer
modelling has been developed. The advantage of the method is that it is
generally applicable and can also reflect non-linear dependencies. This method
allows efficient propagation of uncertainties through any model. It involves first randomly
generating a large set of values of the input quantities. Next, it requires
sequentially evaluating the output quantity (which is determined by the input
quantities through a measurement model). Finally, the dispersion of the
computed output values can be used to evaluate both the estimate and the
uncertainty of output quantity. The latter is taken as being equal to the
standard deviation of the set of computed data.
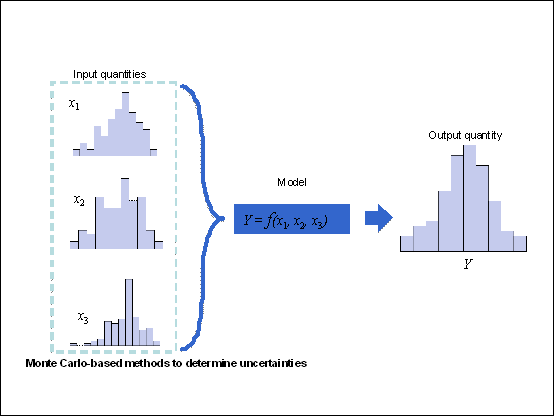
Uncertainties were assessed
by these means from measurements with the mobile NDACC spectroradiometer system
of the Leibniz Universität Hannover (Institut für Meterologie und Klimatologie,
IMUK). The main uncertainty sources are the cosine error and the errors involved
in the absolute calibration. From: Cordero RR. Seckmeyer G. Pissulla D. DaSilva
L. Labbe F. “Uncertainty Evaluation of Spectral UV Irradiance Measurements“
Meas. Sci. Technol. 19 (2008) 1-15.
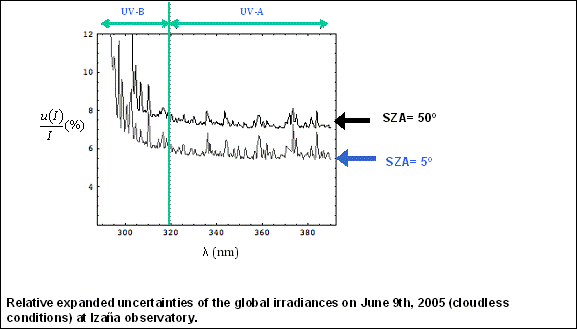
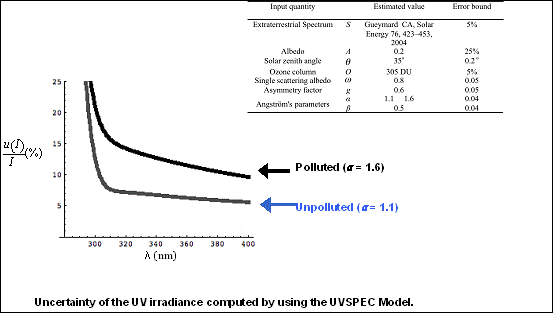
Uncertainties of model calculations can also be determined by this method.
Such models have to use input of atmospheric parameters that are uncertain as well,
which leads to considerable uncertainty as well even for cloudless skies (From:
Cordero RR. Seckmeyer G. Pissulla D. DaSilva L. Labbe F “Uncertainty evaluation
of the spectral UV irradiance evaluated by using the UVSPEC Radiative Transfer Model”
Optics Communications (2007).>
|
Page last modified: Wednesday, 18-Nov-2009 20:39:27 UTC
|
|





